Smart light bulbs are LED bulbs with built-in wireless tech that let you control brightness, color, and schedules from your phone, voice assistant, or smart hub. You can turn lights on or off, dim them, change colors, and set automated scenes from anywhere—no ladder or switch needed.
If you want easier routines, lower energy bills, or more control over mood and safety, smart bulbs make those changes simple. This post shows how they work, the types available, what to watch for when buying, and quick setup tips so you can pick and use the right bulbs for your home.
Key Takeaways
- Smart bulbs let you control lighting remotely and automate daily schedules.
- Different bulb types offer varying colors, connectivity, and compatibility.
- Choose bulbs that match your smart system, security needs, and budget.
Definition of a Smart Light Bulb

Image 2:
A smart light bulb is an LED lamp with built-in electronics and network connectivity that lets you control light from apps, voice assistants, or automation. You can change brightness, color, schedules, and link the bulb to other devices for more control.
What Makes a Light Bulb Smart
A smart bulb has onboard hardware and software that connect it to your home network. It usually supports Wi‑Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, or Z‑Wave so you can send commands from a phone, hub, or voice assistant.
The bulb contains a small processor and firmware that interpret commands, run schedules, and update settings. Many bulbs include a wireless radio and sometimes sensors or motion detection.
You control smart bulbs through a mobile app, voice (Alexa, Google Assistant, Siri), or home automation rules. This lets you dim, set scenes, change color temperature, or turn lights on and off remotely.
Key Features of Smart Light Bulbs
Smart bulbs offer several key features that change how you use home lighting.
- Remote control: Turn lights on/off or adjust settings from anywhere via an app.
- Dimming and color: Set warm-to-cool white or full RGB color on compatible bulbs.
- Scheduling and timers: Create on/off schedules, sunrise/sunset routines, and vacation modes.
- Voice control: Use Alexa, Google Assistant, or Siri to control lights hands-free.
- Energy efficiency and reporting: LEDs use less power than incandescents and some apps show energy use.
- Integration: Link bulbs to motion sensors, cameras, or smart plugs for automation.
These features vary by model. Check whether a bulb needs a hub, which protocols it supports, and whether it works with your voice system.
Comparison With Traditional Light Bulbs
Smart bulbs differ from traditional incandescent or simple LED bulbs in function and cost.
- Function: Traditional bulbs only provide light when powered. Smart bulbs add connectivity, programmability, and remote control.
- Energy and lifespan: Both smart LEDs and standard LEDs are energy efficient. Smart bulbs often list similar lifespans (over 15,000–25,000 hours) but cost more upfront.
- Installation: You install smart bulbs like regular bulbs, but some require a separate hub or bridge for full features.
- Price and value: Smart bulbs cost more per unit but can save energy and add convenience through automation and scheduling.
Choose smart bulbs when you want remote control, automation, or color options. Choose traditional bulbs if you only need basic, low-cost lighting.
How Smart Light Bulbs Work
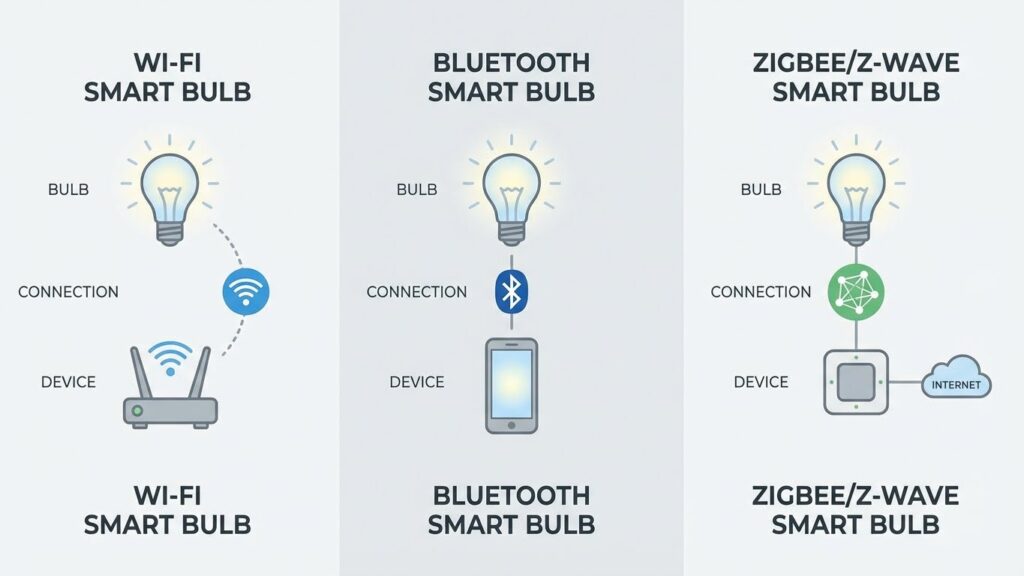
Smart bulbs connect to your devices using wireless signals and a controlling app or voice assistant. They blend LED hardware, a small wireless chipset, and software that lets you change brightness, color, and schedules from your phone or a smart speaker.
Wireless Connectivity and Protocols
Most smart bulbs use Wi‑Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, or Z‑Wave to talk to your phone or hub.
- Wi‑Fi bulbs connect directly to your home router. They let you control bulbs from anywhere with internet, but they use more bandwidth and need a strong router.
- Bluetooth bulbs pair directly with your phone. They use less power and work well for single rooms, but they don’t support remote control unless paired with a hub.
- Zigbee and Z‑Wave bulbs talk to a small hub or bridge. That hub links many devices with low power use and stable mesh networking for larger homes.
Each protocol affects range, battery life of battery-powered devices, and the number of bulbs you can reliably run. Choose the protocol that matches your router strength and whether you want local-only control or cloud access.
Mobile Apps and Voice Control
You control smart bulbs with a mobile app or a voice assistant like Alexa or Google Assistant.
Apps let you turn lights on/off, dim, pick color temperature, set schedules, and create scenes for rooms. They also show firmware updates and energy use on some models.
Voice control uses cloud or local voice processing to send commands to the bulb.
Say phrases like “set living room to 50%” or “make bedroom warm white.” For voice control to work remotely, your bulbs often need a hub or cloud account linked to the voice service.
Types of Smart Light Bulbs
Smart bulbs come in different forms to match how you use light. Some change color, some dim smoothly, and some add motion or daylight sensing so the lights respond automatically.
Color-Changing Smart Bulbs
Color-changing bulbs let you pick millions of colors and adjust white tones from warm to cool. You control them with an app, voice assistant, or a smart-home hub. Use color to set mood for a movie, sync lights to music, or match holiday themes.
These bulbs typically use RGB or RGB+CW LEDs for wide color range and accurate whites. They require a wireless link like Wi‑Fi, Bluetooth, or Zigbee. Expect slightly higher cost than plain bulbs and some need a hub for full features.
When choosing, check maximum brightness (lumens), whether the bulb supports scenes or routines, and compatibility with your voice system. Look for bulbs rated for long life and energy efficiency so you save power while getting rich colors.
Dimmable Smart Bulbs
Dimmable smart bulbs let you fine-tune brightness from near‑off to full output without flicker. You can set schedules, create wake-up routines, or lower light for reading and screen time. Control happens via app sliders, voice commands, or automation rules.
Most smart dimmable bulbs are LED and advertise a lumen output and color temperature range. They use digital control inside the bulb, so they work in standard sockets and don’t need a specialized dimmer switch. Verify that the bulb lists “dimmable” and check for smooth dimming at low levels.
Consider how the bulb integrates with other devices. If you use a physical wall dimmer, make sure it’s compatible or use the switch in a fixed on position and let the app handle dimming to avoid flicker or damage.
Smart Bulbs With Built-In Sensors
Bulbs with built-in sensors add motion detection, daylight sensing, or temperature reporting to the light itself. Motion bulbs turn on when you enter a room and off after a set time. Daylight sensors adjust brightness based on ambient light to save energy.
These bulbs are helpful for hallways, garages, and outdoor fixtures where wiring extra sensors is hard. They mostly connect over Wi‑Fi or Zigbee and can trigger automations in your smart-home system. Check sensor range, sensitivity settings, and whether the bulb can send alerts or integrate with routines.
Keep in mind sensor bulbs may run a little brighter at startup for detection, and some models require a hub for full sensor data in automations. Choose one that matches the detection distance and mounting height of your space.
Benefits of Smart Light Bulbs

Smart bulbs save energy, cut costs, and give you more control over light timing, color, and scenes. They also let you automate routines, sync lights with other devices, and set moods for tasks or entertainment.
Energy Efficiency
Smart bulbs use LED technology that consumes far less power than incandescent or halogen bulbs. You can expect typical smart LEDs to use 8–12 watts for the same brightness a 60–75 watt incandescent produces. That lowers your electricity use and reduces bulb replacement frequency because LEDs last thousands of hours.
Most smart bulbs offer scheduling and dimming. You can set lights to turn off automatically when you leave or dim them at night to save more energy. Some models report energy use in the app, so you can track savings and spot bulbs that use more power than expected.
Convenience and Automation
You control smart bulbs from your phone, voice assistant, or a hub, so you don’t need to touch switches. Create schedules to turn lights on before you get home, or set them to simulate occupancy while you’re away. Automation can link lights to motion sensors, door sensors, or your security camera to turn lights on only when needed.
Many systems support routines like “Good morning” that raise bedroom lights and start a coffee maker. You can also group bulbs by room, control them together, and hand control to family members through shared access in the app.
Custom Lighting Scenes
Smart bulbs let you pick color temperature and RGB colors for different tasks. Use cool white (4000–6500K) for focused work, warm white (2700–3000K) for relaxing, and colored light for parties or movie nights. Most apps let you save scenes so one tap sets all room bulbs to the same levels and colors.
You can fine-tune brightness and color per bulb or by group. Some bulbs integrate with streaming or gaming setups to sync lights with on-screen action. Saved scenes and quick presets make it easy to switch ambiances without adjusting each bulb manually.
Installation and Setup
You will check fixture fit, power needs, and app or hub requirements. Then you will screw in the bulb, connect it to your network or hub, and set up basic controls and schedules.
Compatibility With Fixtures
Confirm the bulb base type (E26, E27, GU10, etc.) and the fixture’s voltage before buying. If your fixture dims, check that the bulb supports dimming and is compatible with the switch. Using a non-dimmable smart bulb on a dimmer can cause flicker or damage.
Look at fixture size and shade clearance. Some smart bulbs are larger than standard bulbs and may not fit enclosed or recessed fixtures. For enclosed fixtures, choose bulbs rated for enclosed use to avoid overheating.
Consider smart hubs and protocols. If you use Zigbee or Z-Wave devices, confirm the hub supports that protocol. Wi‑Fi bulbs need a strong 2.4 GHz signal; they often won’t work on 5 GHz networks. Battery-operated fixtures don’t affect bulb choice.
Initial Configuration
Turn power on and leave the switch in the ON position so the bulb has constant power. Download the manufacturer app and create an account if required. Follow the app’s pairing steps—often you put the bulb into pairing mode by power-cycling it or using a preset blink pattern.
If you use a smart hub (Hue, SmartThings, etc.), add the bulb from the hub’s app instead of the bulb app. Enter your Wi‑Fi SSID and password only when prompted. Name each bulb clearly (e.g., “Kitchen Overhead”) to make voice or app control easier.
Set basic preferences: group bulbs into rooms, choose default brightness, and allow firmware updates. If offered, enable local control or mesh networking for faster response and better reliability.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If the bulb won’t pair, first confirm the switch is ON and the bulb is in pairing mode. Move the bulb closer to the router or hub during setup to avoid weak-signal dropouts. Restart the router or hub if multiple devices fail to connect.
If the bulb flickers or dims unexpectedly, check the wall switch and dimmer compatibility. Replace smart dimmers or use bulbs rated for your dimmer type. For app control delays, reboot the bulb by turning the switch off for 10 seconds, then back on.
If firmware update fails or the bulb becomes unresponsive, reset it to factory settings using the manufacturer’s reset sequence. Re-pair the bulb after reset. Keep the bulb’s firmware and the hub/app software up to date to reduce recurring issues.
Integration With Smart Home Ecosystems
Smart bulbs link to voice assistants, hubs, and other devices to let you control lights by app, schedule, or automation. They can also share status and triggers with locks, sensors, and thermostats to improve comfort and security.
Compatibility With Major Platforms
Check the bulb box for explicit support of Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, or Apple HomeKit before you buy. Alexa and Google work with most Wi‑Fi and hub-based bulbs; HomeKit requires a certified chip or a bridge.
Look for protocol labels: Wi‑Fi, Zigbee, or Z‑Wave. Wi‑Fi bulbs talk directly to your router and phone. Zigbee and Z‑Wave bulbs usually need a hub (Philips Hue Bridge, Samsung SmartThings) but use less network bandwidth.
Also check app features: scene creation, schedules, and remote access vary by vendor. If you use multiple brands, pick bulbs that list the same platform compatibility to avoid juggling apps or buying extra bridges.
Connecting With Other Smart Devices
Use routines or automations in your smart home app to link bulbs with sensors, locks, and thermostats. For example, set a motion sensor to turn lights on at 50% brightness at night, or have your thermostat trigger warm lighting when it shifts to evening mode.
Group bulbs into rooms or zones so a single command controls multiple fixtures. That helps with whole-room dimming and scene recall.
If you mix ecosystems, use a central hub or a platform like SmartThings or Home Assistant to translate commands across brands. Test automations after setup to confirm timing and conditions work as you expect.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Smart bulbs can collect and transmit data, and they connect to your home network. You need to control who can access them and keep firmware and accounts up to date to reduce risk.
Data Protection Measures
You should change default passwords on any bridge, app, or cloud account that controls bulbs. Use a strong, unique password and enable two-factor authentication when available.
Limit the data the app can access. Turn off permissions the app does not need, such as precise location or contacts. Review the vendor’s privacy policy to know what telemetry they collect and how long they keep it.
Place smart bulbs and their control hubs on a separate guest or IoT network if your router supports it. This isolates them from your computers and phones and reduces the chance of lateral movement if a device is compromised.
Regularly update the bulb firmware and the controlling app. Updates often fix security bugs that attackers could exploit.
Potential Vulnerabilities
Smart bulbs use Wi‑Fi, Zigbee, or Bluetooth. Each protocol has specific risks: weak Wi‑Fi passwords let attackers join your network, and insecure Bluetooth pairing can allow nearby access. Older Zigbee firmware has known exploits that let attackers send fake commands.
Unpatched devices are the main threat. Attackers can use a vulnerable bulb to scan your internal network or to create access points into more sensitive devices.
Public cloud integrations add risk when the vendor’s servers are breached. Disable cloud features you don’t need and prefer local control modes if the bulb supports them. Monitor your network for unknown devices and unexpected traffic from your bulbs so you can detect problems early.
Latest Innovations in Smart Lighting
Smart bulbs now adjust color and brightness automatically and track energy use to save money. You can expect lights that change with your schedule and give clear data on power consumption.
Adaptive Lighting Technology
Adaptive lighting changes color temperature and brightness throughout the day to match natural light. Your bulbs shift from cool, bright white in the morning to warmer, softer tones in the evening. This helps you wake up, focus during work, and wind down before bed.
Many adaptive systems use built-in clocks, sunrise/sunset data, or ambient light sensors to make adjustments. Some bulbs learn your routines and suggest scenes based on when you use rooms. You can still set manual schedules in the app or use voice commands with assistants like Alexa, Google Assistant, or Siri.
Look for features such as circadian modes, motion-triggered boosts, and scene syncing across multiple bulbs. These let your lighting support sleep patterns, reduce eye strain, and create consistent mood lighting across rooms.
Energy Monitoring Features
Energy monitoring shows how much power each bulb uses and estimates cost over time. Your app can display hourly, daily, or monthly usage so you see when lights waste energy.
Some bulbs provide real-time watts and historical charts. You can set alerts for unusually high use and compare normal vs. peak consumption. This helps you spot faulty bulbs, optimize schedules, and justify switching to LEDs or lower brightness settings.
If you want deeper control, choose bulbs or hubs that export usage data or integrate with home energy platforms. That lets you combine lighting data with HVAC or appliance usage to reduce overall electricity bills.
Choosing the Right Smart Light Bulb
Pick bulbs that match your sockets, control needs, and budget. Focus on connection type, color and brightness options, smart-home compatibility, and brand reliability.
Factors to Consider
Look at the bulb base (E26, E27, GU10) to make sure it fits your fixtures. Check watt-equivalent and lumens for brightness — 800 lumens roughly equals a 60W incandescent.
Decide between tunable white (warm to cool) and full color (RGB). Tunable white helps with tasks and sleep cycles; color gives mood and party effects. Confirm dimming works smoothly without a separate dimmer switch.
Check connection type: Wi‑Fi bulbs connect directly to your router; Zigbee or Z‑Wave bulbs require a hub but use less bandwidth and often respond faster. Bluetooth works for single-room control but limits remote access.
Verify smart-home integration: look for compatibility with Alexa, Google Assistant, or Apple HomeKit. Read app reviews for stability and features like scenes, schedules, and firmware updates.
Factor price and energy use. Compare estimated yearly energy cost and whether the bulb supports power-saving modes. Consider warranty length and return policy before buying.
Popular Brands and Products
Philips Hue offers wide compatibility, bright tunable whites, and rich color options. These bulbs often require a Hue Bridge for full features but work well in multi-room setups.
LIFX bulbs provide high color saturation and connect via Wi‑Fi, so you can skip a hub. They tend to be a bit pricier but offer strong app control and built-in effects.
Sengled sells budget-friendly bulbs with both Wi‑Fi and Zigbee models. Their bulbs perform well for basic dimming and scheduling and pair easily with many hubs.
Wyze and TP‑Link Kasa give solid value for Wi‑Fi bulbs with straightforward apps and Alexa/Google support. They’re good if you want low cost and no hub.
When choosing, match features to your setup: hub required vs. hubless, color needs, and whether you value app polish or lower price.
FAQs
What does a smart light bulb do and how does it connect?
A smart bulb lets you control brightness, color, and schedules from your phone or voice assistant. Most connect via Wi‑Fi, Bluetooth, or a smart home hub so they can talk to other devices.
Are smart bulbs energy efficient?
Yes. Most smart bulbs use LED technology, which uses less energy than old incandescent bulbs. You can also set timers or automations to cut wasted power.
Do I need a hub or special wiring?
Not always. Some bulbs work directly with Wi‑Fi or Bluetooth. Others use hubs like Zigbee or Z‑Wave to link many devices; check the bulb’s requirements before buying. See compatibility info at the Zigbee Alliance or a manufacturer’s support page for clear guidance.
Can anyone install smart bulbs?
You can install them like a regular bulb in most fixtures. Then download the maker’s app to set them up. If you use a hub or complex automations, you might need extra steps.
Are smart bulbs secure and private?
They can be secure if you keep firmware updated and use strong Wi‑Fi passwords. Choose reputable brands and review their privacy policies to know what data they collect.
Will smart bulbs work during a power outage?
No. Like regular bulbs, smart bulbs need power to operate. Consider a smart switch or backup power if you need lights during outages.
Conclusion
Smart light bulbs give you more control over your home lighting. You can change brightness, color, and schedules from your phone or with voice commands.
They can save energy compared with older bulbs, especially if you use scheduling and automation. Some bulbs also work with smart hubs and other devices for deeper home integration.
Choose bulbs that match your setup: Wi‑Fi models work well alone, while Zigbee or Z‑Wave bulbs work best with hubs. Check brightness (lumens), color options, and whether you need a bridge or app.
Think about privacy and security when connecting lights to your network. Keep firmware updated and use strong passwords to reduce risks.
If you want simple convenience, look for easy setup and reliable apps. If you want advanced scenes and automations, pick bulbs that support your preferred smart home platform.
Benefits at a glance:
- Control lights remotely and by voice
- Save energy with scheduling and LED efficiency
- Create scenes and adjust color for mood or tasks
You can start small with one room and expand as you see the value. Smart bulbs are an easy, low‑risk way to add smart features to your home.
